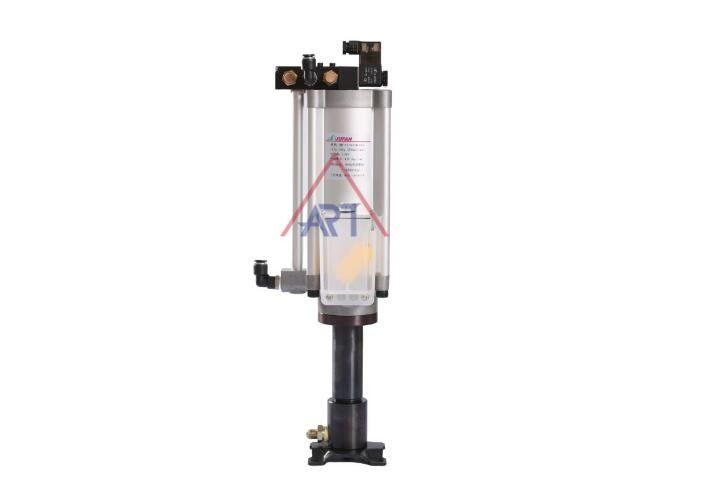
Product Description
1.Working pressure: The pump can operate within a pressure range of 0.4 megapascals (MPa) to 0.6 MPa. This can also be expressed as 4 kilograms-force per square centimeter (kgf/cm²) to 6 kgf/cm². The compressed air used to filter the pump should also be within this pressure range.
2.Transmission oil: The pump is designed to work with a specific viscosity grade of oil, which is ISO VG32 or an equivalent viscosity grade.
Working temperature: The pump can operate within a temperature range of 0 degrees Celsius to 60 degrees Celsius.
Split out quantity: The pump can output four different quantities of oil, which are 150cc, 110cc, 70cc, and 50cc.
Voltage: The pump can operate with three different voltage levels, which are DC24, AC110, and AC220.
Suitable for direct drive spindle, motor built-in spindle, etc., special for high-speed cutting:
The hydraulic motor or spindle is designed to be used in direct drive applications, such as motor built-in spindles.
The motor or spindle is specifically designed for high-speed cutting, indicating that it is capable of operating at high speeds while maintaining its performance and reliability.
Order Form
BMV--10--U--16--M--70--MA
1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6)
| BMV:Supercharged knife punch pneumatic cylinder |
| 1) |
Diameter |
10:Ø100 12:Ø125 |
| 2) |
Applicable model |
U:used to MC |
| 3) |
Oil pressure ratio |
11=11:1 12=12:1 16=16:1 25=25:1 30=30:1 39=39:1 51=51:1 |
| 4) |
|
M:With hydraulic detection device
N:No hydraulic detection device
|
| 5) |
Spit volume |
50cc, 70cc, 110cc, 150cc,etc |
| 6) |
Mounting type |
FA:vertical type,LB:horizontal type |
Our production:

Hydraulic cylinders and hydraulic motors are both crucial components of hydraulic systems, but they serve different purposes and operate in distinct ways.
Hydraulic Cylinder:
As described earlier, a hydraulic cylinder is a mechanical actuator that converts hydraulic energy into linear mechanical force and motion.
It consists of a cylindrical barrel, a piston, seals, and end caps.
Hydraulic cylinders are primarily used for generating linear motion, such as lifting, pushing, or pulling heavy loads.
They operate by pressurizing hydraulic fluid on one side of the piston, which causes the piston to move, thus generating linear force.
Hydraulic Motor:
A hydraulic motor is a mechanical device that converts hydraulic energy into rotary mechanical motion.
It typically consists of a housing, an output shaft, internal gears or pistons, and inlet/outlet ports.
Hydraulic motors are used to drive machinery, such as pumps, conveyors, winches, and other rotary equipment.
They operate by receiving pressurized hydraulic fluid from a pump, which causes the internal components (gears or pistons) to rotate, thus generating rotary motion at the output shaft.
While hydraulic cylinders produce linear motion, hydraulic motors produce rotary motion. However, both components rely on the same principles of hydraulic fluid pressure to generate mechanical movement. They are often used together within hydraulic systems to achieve complex mechanical tasks, such as in hydraulic excavators or hydraulic presses, where both linear and rotary motions are required.
FAQ
Q1: We have our own factory and can provide the best price and service.
Q2: We accept customization or non-standard products.
Q3: The MOQ depends on the customer's needs, and trial orders are welcome before mass production.
Q4: The delivery time is 7 days if the company has stock, and 15-30 working days if we don't have stock. However, the delivery time also depends on the quantity and requirements of the products.
Q5: The company's payment terms are T/T.
Q6: The company does not provide samples.
How to choose the hydrualic cylinder?
Choosing the right hydraulic cylinder involves several key considerations to ensure it meets the requirements of your specific application. Here are the steps to guide you through the selection process:
1. Determine the Application Requirements
Load Requirements: Calculate the force needed for the application. This depends on the load you need to move or lift. Force (F) is calculated using the formula
Stroke Length: Measure the distance the piston needs to travel.
Mounting Style: Determine the appropriate mounting style based on the application. Common styles include flange, clevis, trunnion, and spherical bearings.
Speed Requirements: Identify the speed at which the piston needs to move.
2. Select the Cylinder Type
Single-Acting Cylinders: These have one port and extend in one direction under hydraulic pressure, with retraction powered by an external force such as a spring.
Double-Acting Cylinders: These have two ports and can extend and retract with hydraulic pressure.
3. Calculate the Cylinder Size
Bore Size: The diameter of the cylinder bore affects the force output. A larger bore diameter produces more force.
Rod Size: The diameter of the rod affects the cylinder’s strength and buckling resistance. Ensure the rod is strong enough for the application load.
Piston Area: Use the bore size to calculate the piston area, which determines the force the cylinder can exert.
4. Consider the Operating Conditions
Pressure Rating: Ensure the cylinder can handle the maximum operating pressure of your hydraulic system.
Temperature Range: Check the cylinder’s temperature rating to ensure it can operate under your environmental conditions.
Fluid Compatibility: Ensure the cylinder materials are compatible with the hydraulic fluid you plan to use.
5. Review the Cylinder Features
Cushioning: Some applications require end-of-stroke cushioning to absorb the shock when the piston reaches the end of its travel.
Seals: Choose appropriate seals based on the operating environment to prevent leaks and contamination.
Materials: Select the cylinder material (e.g., steel, aluminum) based on strength requirements and environmental conditions.
6. Evaluate the Manufacturer and Cost
Manufacturer Reputation: Choose a reputable manufacturer known for quality and reliability.
Cost: Compare costs but consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and longevity, rather than just the initial purchase price.
Conclusion:
Choosing the right hydraulic cylinder involves understanding the specific needs of your application, calculating the required force and stroke, and ensuring compatibility with your hydraulic system. By considering these factors, you can select a cylinder that delivers reliable and efficient performance.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!